 15 December 2025
15 December 2025
Agentic AI vs. Generative AI: Guide to What They Are & How to Use Them
Artificial Intelligence (AI) has become one of the defining technologies of our time. It's often imagined as a field of intelligent systems capable of learning from data, adapting behavior, and performing tasks that typically require human intelligence. But in reality, AI is a vast field with several subdomains, each with its own purpose, design, and functionality. Among the most prominent of these are generative AI and agentic AI.
What is Generative AI?
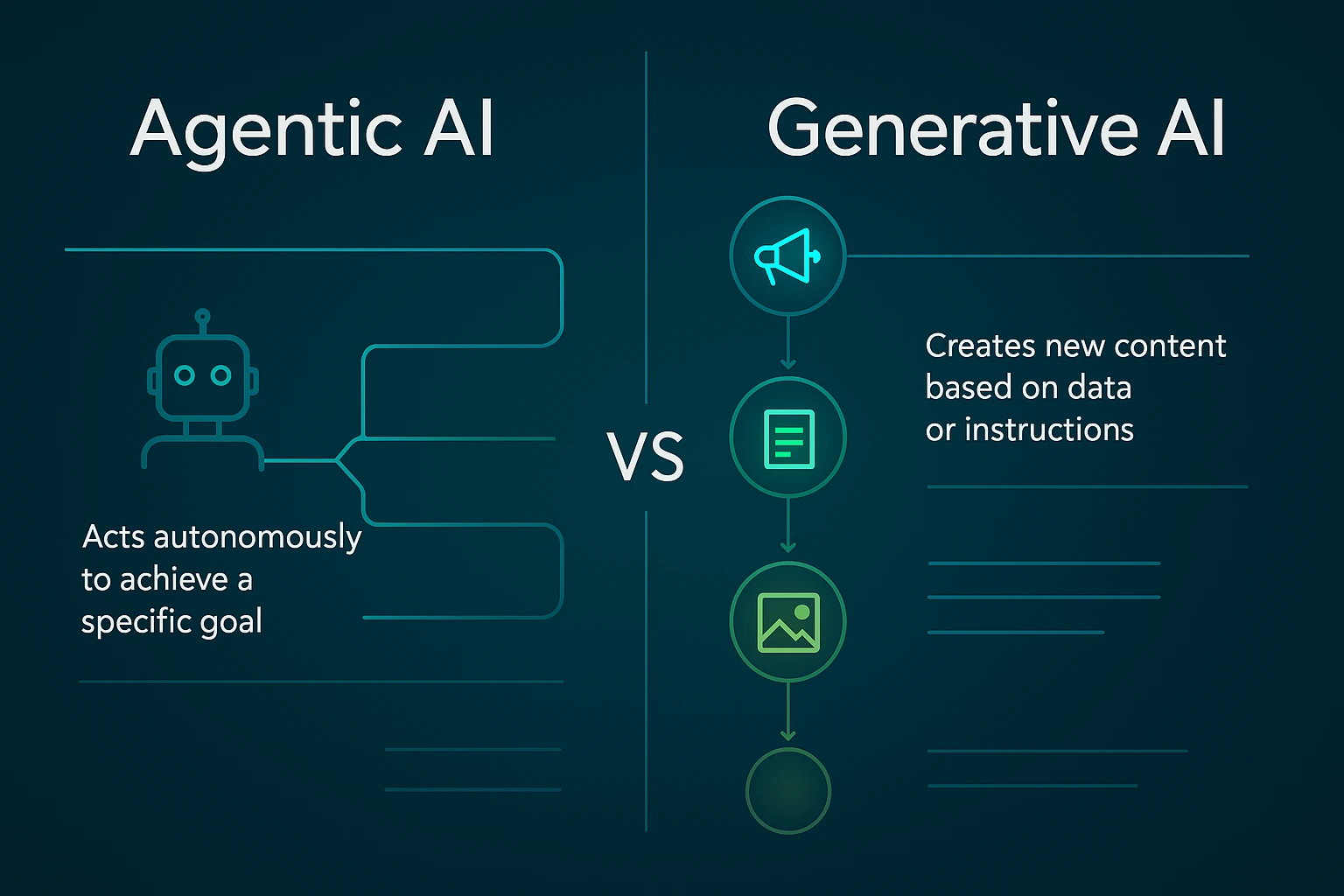
Generative AI is the creative arm of artificial intelligence that uses machine learning and large language models (LLMs) to generate original outputs such as text, images, music, video, or even code based on the data it is trained on.
These systems identify patterns and relationships across massive datasets, learning the structure of language, design, or sound. Once trained, they can generate new content that resembles what humans create. For example, a gen AI model like ChatGPT can write essays, compose emails, or produce code, DALL·E can create images, and tools like Midjourney generate artistic visuals.
At the technical level, gen AI relies heavily on deep learning, where neural networks simulate aspects of human cognition. It is primarily reactive in the sense that it responds to a user's prompt or request. Yet, the results often appear strikingly human, which is why generative AI has become one of the most talked-about technologies of the decade.
Features of Generative AI
Before looking at the use cases, it's essential to understand the features that make generative AI distinctive. These are:
- Content Creation: Generative AI excels in creating high-quality content from textual prompts. Whether writing marketing copy, generating blog posts, or drafting software code, it can produce structured and contextually relevant material.
- Data Analysis: Besides creation, generative AI models can analyze enormous datasets, extract insights, and highlight trends. By identifying patterns within complex systems, they support decision-making in fields like supply chain optimization and predictive analysis.
- Adaptability: A defining trait of generative AI is its ability to refine its output based on user feedback. The system learns through interaction, adjusting tone, structure, or depth in real time.
- Personalization: In industries such as retail and e-commerce, generative AI powers personalized recommendations by analyzing user behavior and preferences. It tailors experiences by suggesting a product, writing a response, or curating relevant content, thus making interactions feel more human and specific to needs.
Use Cases of Generative AI
Generative AI has reshaped workflows across multiple sectors. Its flexibility allows organizations to apply it to diverse objectives such as:
1. Content Creation:
Businesses are using generative AI to produce keyword-optimized blogs, website pages, social
media, and product descriptions that improve visibility and traffic. For example, digital
agencies deploy gen AI models to maintain content velocity without compromising quality.
2. Marketing and Sales:
Sales teams benefit from AI-driven chatbots and virtual
assistant systems that automate responses, generate outreach messages, and manage
administrative tasks. These tools free human teams to focus on strategy and client engagement.
3. Product Design and Development:
Design-focused organizations use generative AI to create new product concepts. By analyzing
consumer data and market trends, the technology helps designers visualize ideas faster and
refine prototypes efficiently.
4. Customer Support Automation:
E-commerce platforms and service providers use generative AI chatbots to handle real-time queries, automate
responses, and provide troubleshooting. These systems enhance service quality while reducing
manual effort.
What is Agentic AI?
Agentic AI refers to intelligent systems that can make decisions, take actions, and achieve objectives autonomously with limited supervision. Therefore, while generative AI is about creating, agentic AI is about acting.
It blends machine learning, reinforcement learning, and reasoning capabilities to operate independently. Unlike generative systems that wait for human prompts, agentic AI acts proactively to fulfill defined goals. It combines the adaptive nature of large language models with logical decision-making allowing it to assess real-world situations and choose the best course of action.
Examples include autonomous vehicles navigating traffic, robots managing logistics, and virtual assistants scheduling meetings or automating enterprise processes. Precisely, agentic AI represents the operational intelligence that executes tasks rather than merely suggesting or creating.
Agentic AI and AI Agents - Do They Mean the Same?
Although the terms sound similar, Agentic AI and AI agents are not similar.
Agentic AI is the framework that defines how autonomous systems operate and make decisions and within this framework AI agents exist who are basically individual components or modules responsible for carrying out specific tasks.
For instance, in a smart home powered by agentic AI, multiple AI agents control separate systems like lighting, temperature, and energy use. Together, they collaborate to meet the homeowner's overall goal. Each agent functions semi-independently but aligns under the agentic system's broader purpose.
Features of Agentic AI
The following are the features that make the technology of agentic AI stand apart:
- Decision-Making: Agentic AI evaluates situations, interprets data, and selects actions to achieve defined goals. Its capacity for autonomous reasoning allows it to manage complex, multi-step processes.
- Problem-Solving: At its core, agentic AI follows a four-step process—perceive, reason, act, and learn. It perceives data from its environment, uses reasoning models (often built on large language models) to analyze it, acts using connected tools or devices, and learns from outcomes to refine future decisions.
- Autonomy: Autonomy is the hallmark of agentic AI. It performs functions without constant human intervention, making it valuable for automated workflow management and operational optimization.
- Interactivity: Unlike traditional AI, which responds to inputs, agentic AI interacts dynamically with its surroundings. It collects live data, senses environmental changes, and modifies actions accordingly—for example, how a self-driving car adjusts to road conditions.
- Planning: Agentic AI handles long-term and multi-step goals. It can design execution strategies, assign tasks to AI agents, and evaluate progress toward outcomes.
Use Cases of Agentic AI
1. Customer Service:
Agentic AI systems have evolved beyond static
chatbots. They understand user intent, interpret emotional tone, and autonomously
resolve issues. Businesses use them to automate data handling, freeing human teams for
higher-value tasks.
2. Healthcare:
Healthcare
applications rely on agentic AI for monitoring, diagnostics, and patient care.
3. Automated Workflow Management:
Organizations deploy agentic AI to streamline operations from reordering supplies to optimizing
logistics. In logistics, for instance, an agentic system can adjust delivery routes
automatically based on real-time conditions.
4. Financial Risk Management:
Banks and fintech platforms use agentic AI to assess market trends and autonomously adjust
portfolios or credit policies. It acts as a decision-making layer that continuously optimizes
financial outcomes based on live data.
Key Differences Between Agentic AI and Generative AI
| Aspect | Generative AI | Agentic AI |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Creates new content (text, image, video, code) | Acts autonomously to achieve goals |
| Nature | Reactive - responds to user prompts | Proactive - takes initiative to fulfill objectives |
| Learning Approach | Learns from existing data to generate outputs | Learns from real-time interaction and feedback |
| Core Technology | Large language models, machine learning, and deep learning | Machine learning, reinforcement learning, decision modeling, and environmental sensing |
| Interaction with Environment | Limited - operates within trained data boundaries | Dynamic - constantly adapts to external input |
| Scope of Tasks | Narrow, creative, or expressive outputs | Broad, goal-oriented and multi-step processes |
| Examples | ChatGPT, DALL·E, Midjourney | Autonomous vehicles, robotic process automation, smart assistants |
| Use in Enterprises | Marketing, content creation, and communication | Operations, automated workflow management, logistics, and decision systems |
The Intersection of Generative AI and Agentic AI
Though their functions differ, generative AI and agentic AI are not separate worlds. In practice, they often work together to create end-to-end intelligent ecosystems.
Take the example of a virtual assistant in customer service. The agentic AI component manages real-time decision-making, routing issues, prioritizing requests, and acting to resolve them. Simultaneously, the generative AI element crafts personalized responses and contextually accurate messages.
This partnership also extends to robotics and manufacturing. A robot chef, for instance, could use generative AI to design new recipes while the agentic AI executes the cooking process autonomously, adjusting heat, timing, and portions. Together, they represent the merger of creativity and autonomy, creation with action.
The Future of Artificial Intelligence
As artificial intelligence continues to evolve, the line between generative AI and agentic AI is becoming less distinct. The next wave of innovation lies in intelligent systems that can both create and act, where generative AI generates context, and agentic AI executes actions based on that context.
This combined intelligence is already being applied in enterprise communication and automated workflow management, where businesses seek to simplify operations without losing human-like interaction. The future of AI will not just be about producing content or completing isolated tasks but it will be about systems that think, act, and deliver results seamlessly.
Kiksy represents this convergence in a real, operational form by standing at this intersection, helping businesses adopt AI that's both creative and actionable.
By merging generative AI's ability to understand and respond in natural language with agentic AI's capacity to make autonomous decisions, Kiksy allows businesses to manage customer journeys intelligently. From retail and real estate to healthcare and hospitality, it delivers goal-driven automation while maintaining contextual accuracy and human-like communication. Visit our website to explore what Kiksy offers.
Kavita Jha
Chief Executive Officer
Kavita has been adept at execution across start-ups since 2004. At KiKsAR Technologies, focusing on creating real life like shopping experiences for apparel and wearable accessories using AI, AR and 3D modeling.
